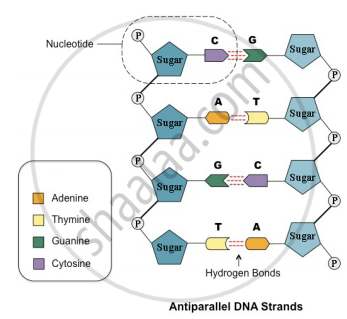
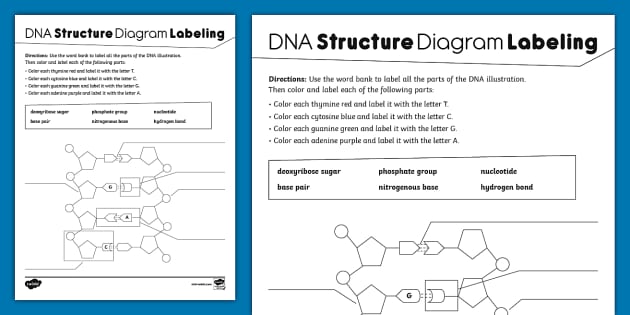
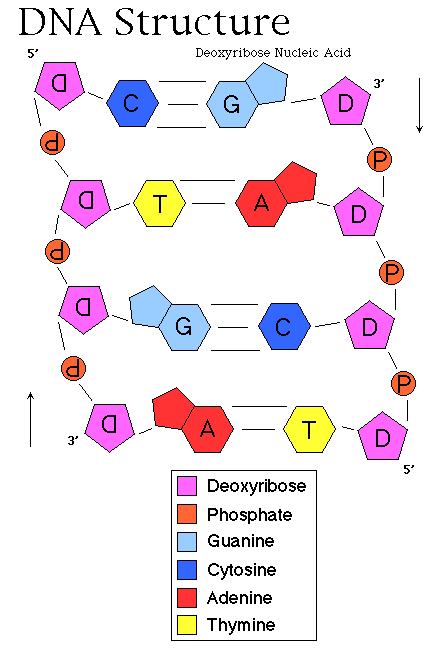
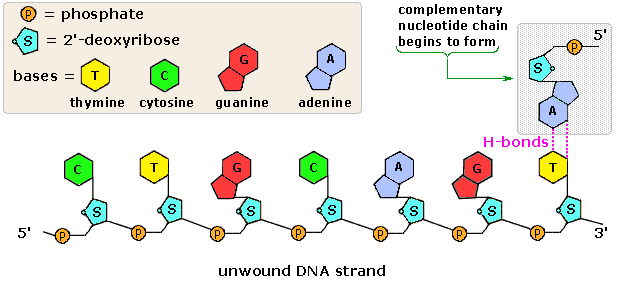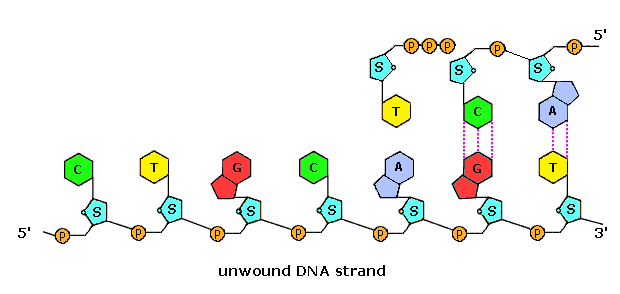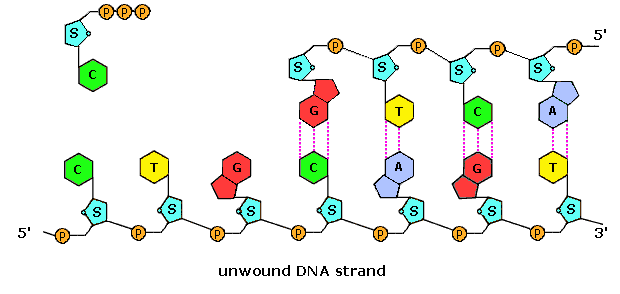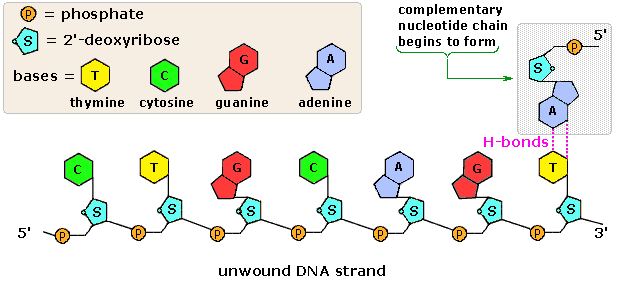
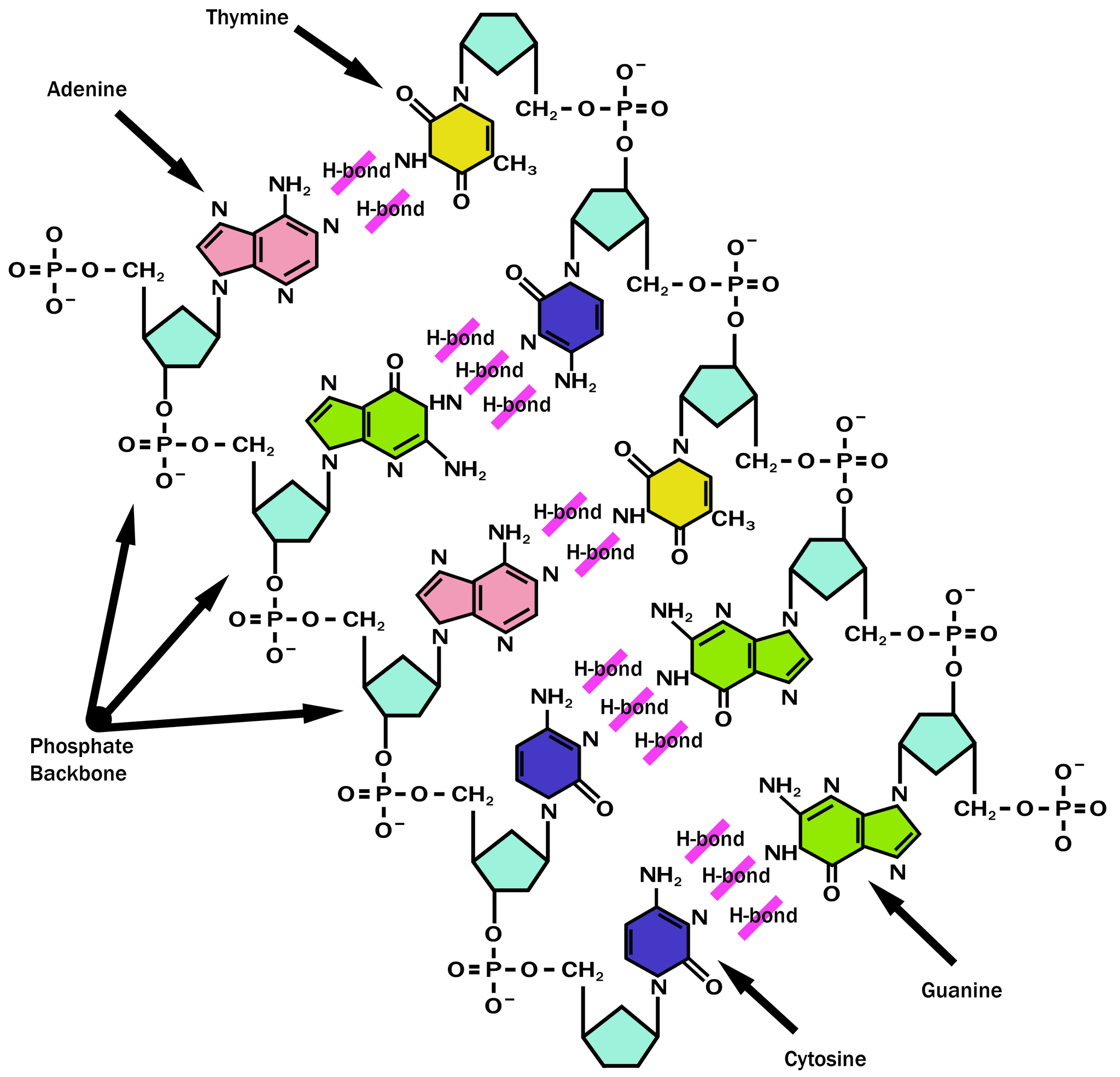
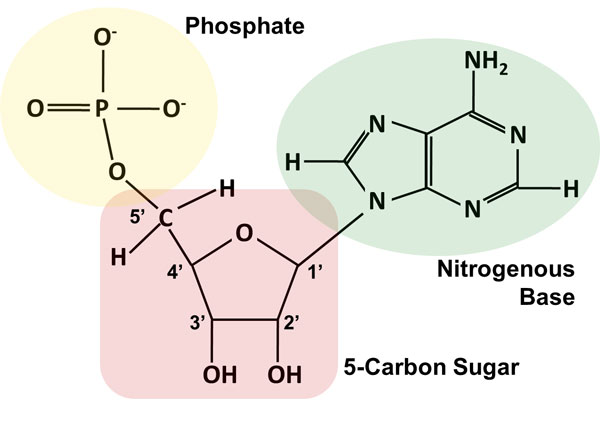
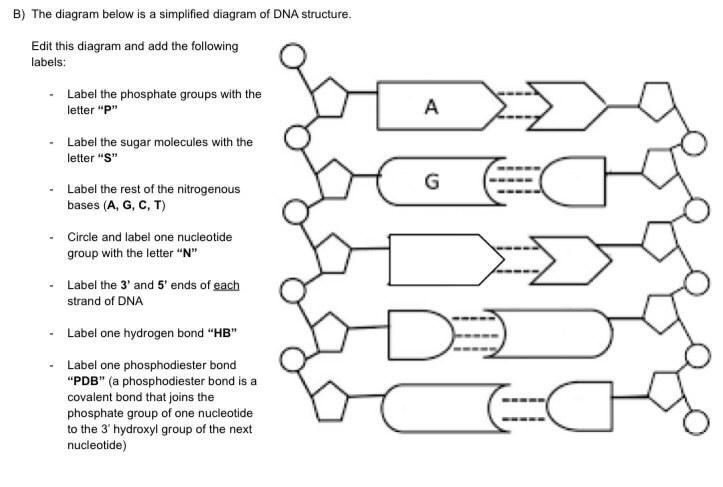
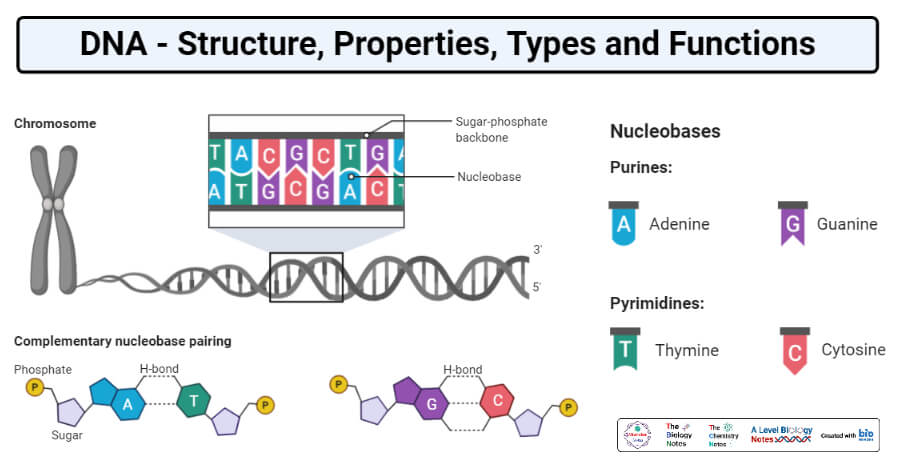
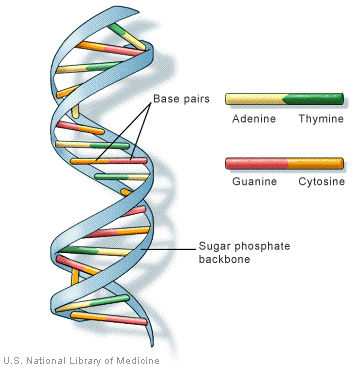
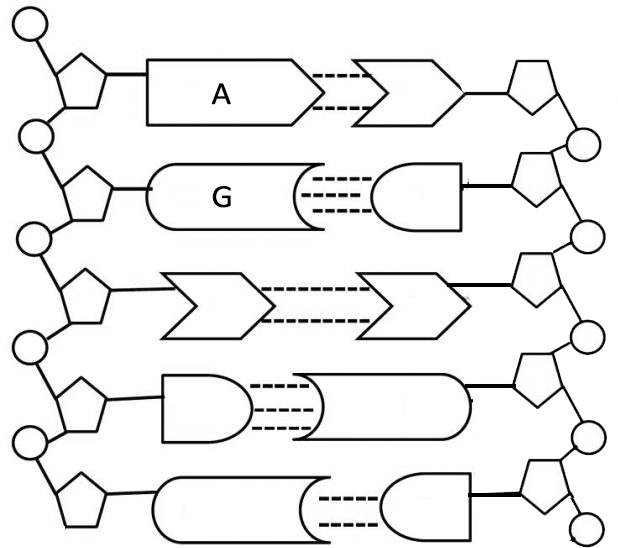
41 dna labeling diagram
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase - Wikipedia WebTerminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma cells. TdT adds N-nucleotides to the V, D, and J exons of the TCR … › difference › Transcription_vsTranscription vs Translation - Difference and Comparison | Diffen For Transcription, RT-PCR, DNA microarray, In-situ hybridization, Northern blot, RNA-Seq is quite often used for measurement and detection. For Translation, western blotting, immunoblotting, enzyme assay, Protein sequencing, Metabolic labeling, proteomics is used for measurement and detection.
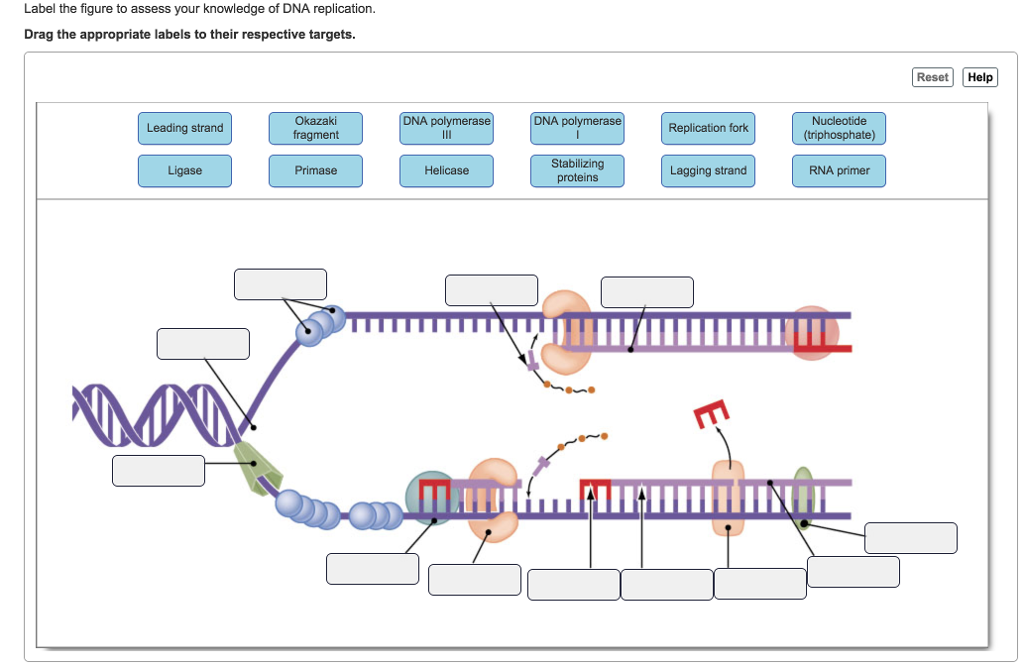
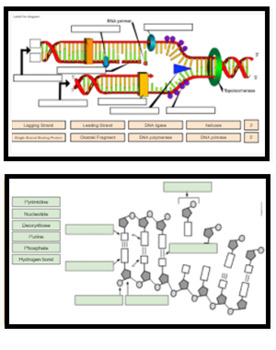
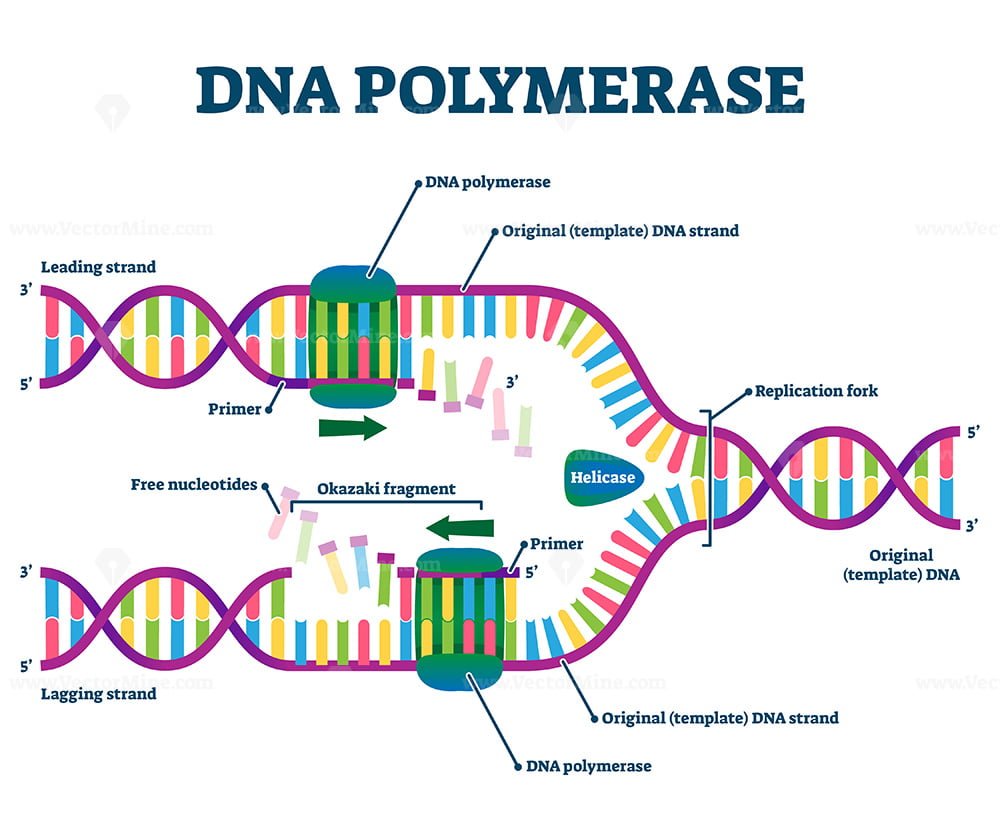
DNA Replication Labeling Diagram | Quizlet WebDNA Replication Labeling. Flashcards. Learn. Test. Match. Flashcards. Learn. Test. Match. Created by. Kimberly_McGuffie. Terms in this set (11) Single Stranded Binding Protein. Binds to and stabilizes single-stranded DNA until it can be used as a template. Helicase. An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication. Okazaki …
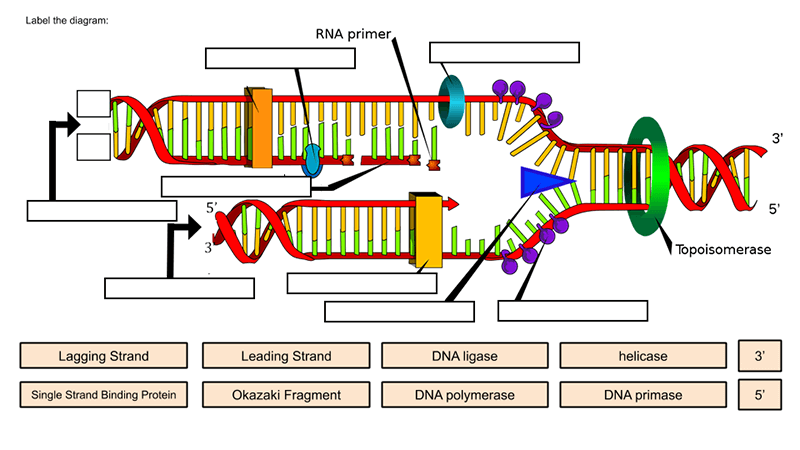
Dna labeling diagram
Genetically modified foods | Food Standards Agency WebGenetically modified foods can be defined as organisms (i.e. plants or animals) in which the genetic material (DNA) has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural recombination. GM stands for 'genetic modification' or 'genetically modified'. It’s the process of altering the genes of a living thing. Genes carry the instructions for all … Ionizing radiation - Wikipedia WebAlthough DNA is always susceptible to damage by ionizing radiation, the DNA molecule may also be damaged by radiation with enough energy to excite certain molecular bonds to form pyrimidine dimers. This energy may be less than ionizing, but near to it. A good example is ultraviolet spectrum energy which begins at about 3.1 eV (400 nm) at close to … en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Transcription_(biology)Transcription (biology) - Wikipedia Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples.
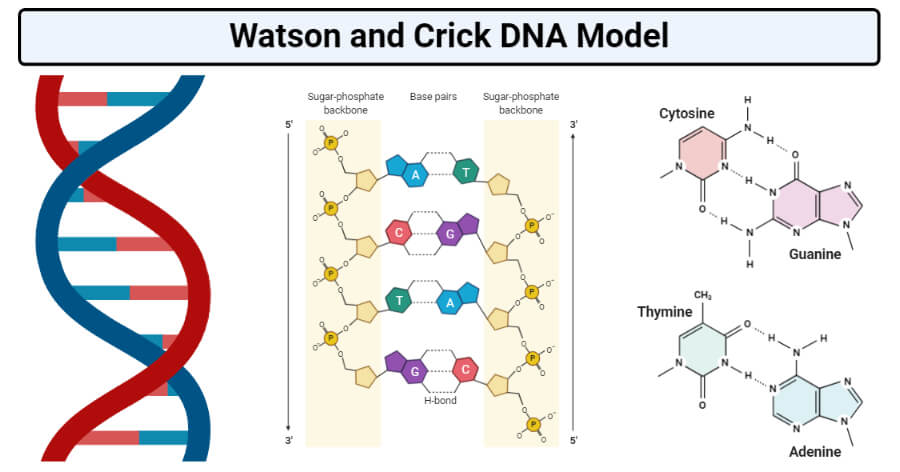
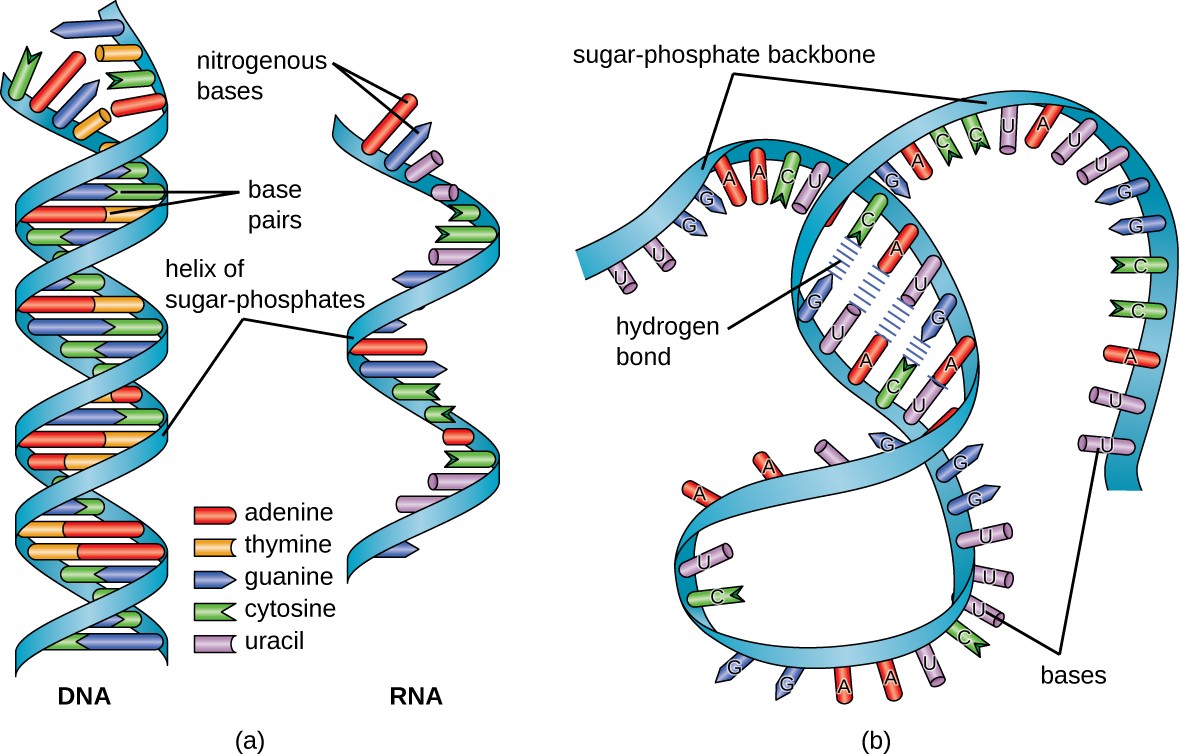
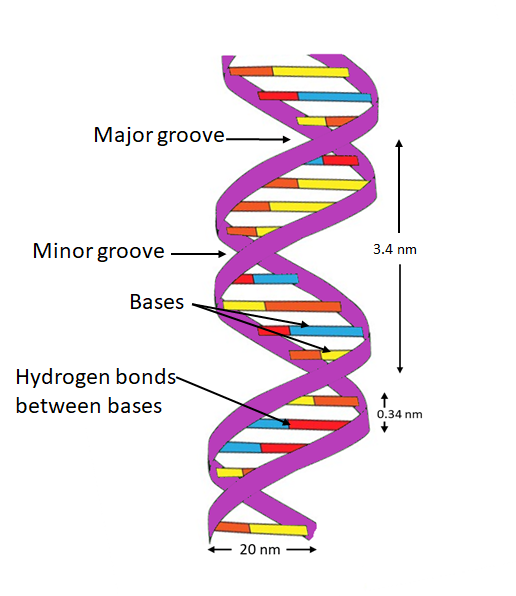
Dna labeling diagram. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › DNA_nanotechnologyDNA nanotechnology - Wikipedia Properties of nucleic acids. Nanotechnology is often defined as the study of materials and devices with features on a scale below 100 nanometers.DNA nanotechnology, specifically, is an example of bottom-up molecular self-assembly, in which molecular components spontaneously organize into stable structures; the particular form of these structures is induced by the physical and chemical ... Join LiveJournal WebPassword requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols; Transcription vs Translation - Difference and Comparison | Diffen WebFor Translation, western blotting, immunoblotting, enzyme assay, Protein sequencing, Metabolic labeling, proteomics is used for measurement and detection. Crick’s central dogma: DNA ---> Transcription ---> RNA ---> Translation ---> Protein Genetic code used during translation: References. wikipedia:Transcription (genetics) Gene expression - Wikipedia WebGene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect.These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA …
› safety-hygiene › geneticallyGenetically modified foods | Food Standards Agency Genetic modification can also be achieved by altering DNA which is the material that genes are made from. The way a gene works can now be changed by 'switching it off' to stop something happening. For example, a gene involved in softening a fruit could be switched off. Transcription (biology) - Wikipedia WebTranscription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the … › cells › cell_modelInteractive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive When a cell is dividing, the nuclear chromatin (DNA and surrounding protein) condenses into chromosomes that are easily seen by microscopy. For a deeper understanding of genetics, visit our companion site, GeneTiCs Alive! Nucleolus: The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the ... DNA Color Clustering: The Leeds Method for Easily ... - Dana … Web23/08/2018 · Unsure of how other people were sorting their Shared Matches from AncestryDNA, I developed my own method: the Leeds Method of DNA Color Clustering. This simple and quick method helps you easily visualize how your close cousins are related to you and each other. I created this method while working with an adoptee, and it …
Diagram Quiz on Neuron Structure and Function (Labeling Quiz) WebThis labelled diagram quiz on Neuron is designed to assess your basic knowledge in Structure and Function of Neuron. Choose the best answer from the four options given. When you've finished answering as many of the questions as you can, scroll down to the bottom of the page and check your answers by clicking ' Score '. Percentage score will be … en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Gene_expressionGene expression - Wikipedia A very important modification of eukaryotic pre-mRNA is RNA splicing.The majority of eukaryotic pre-mRNAs consist of alternating segments called exons and introns.During the process of splicing, an RNA-protein catalytical complex known as spliceosome catalyzes two transesterification reactions, which remove an intron and release it in form of lariat structure, and then splice neighbouring ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Terminal_deoxynucleotidylTerminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase - Wikipedia Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma cells. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Transcription_(biology)Transcription (biology) - Wikipedia Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples.
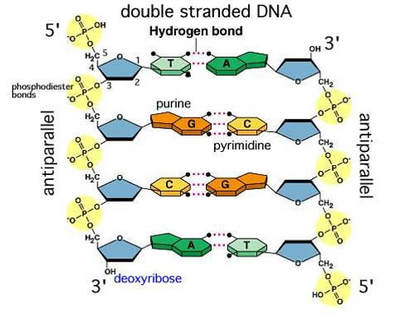
Ionizing radiation - Wikipedia WebAlthough DNA is always susceptible to damage by ionizing radiation, the DNA molecule may also be damaged by radiation with enough energy to excite certain molecular bonds to form pyrimidine dimers. This energy may be less than ionizing, but near to it. A good example is ultraviolet spectrum energy which begins at about 3.1 eV (400 nm) at close to …
Genetically modified foods | Food Standards Agency WebGenetically modified foods can be defined as organisms (i.e. plants or animals) in which the genetic material (DNA) has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural recombination. GM stands for 'genetic modification' or 'genetically modified'. It’s the process of altering the genes of a living thing. Genes carry the instructions for all …


















Komentar
Posting Komentar